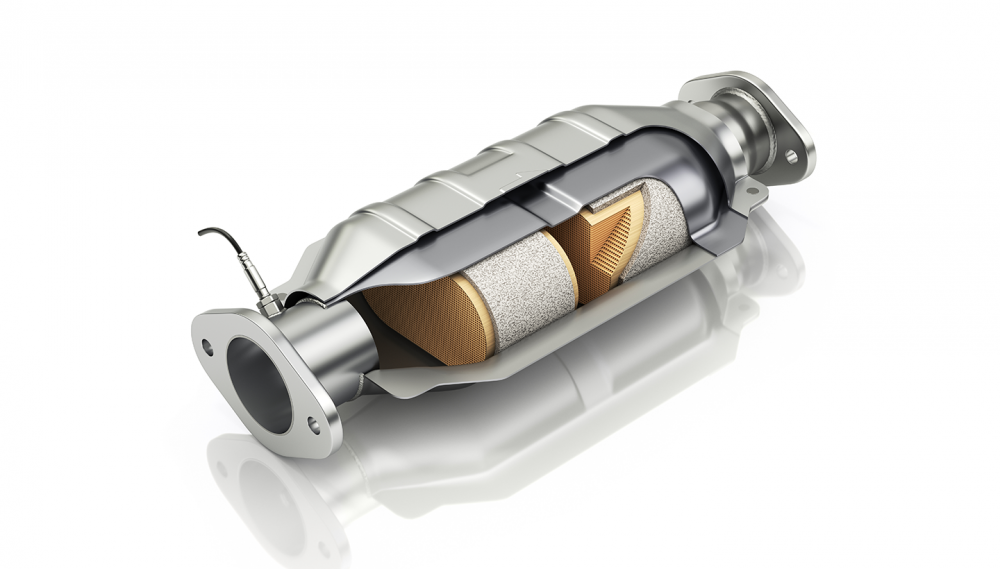
The catalyst is a key component of a car’s exhaust system, responsible for reducing the toxicity of emissions. Its main task is to convert harmful substances, such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), into less harmful substances: carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
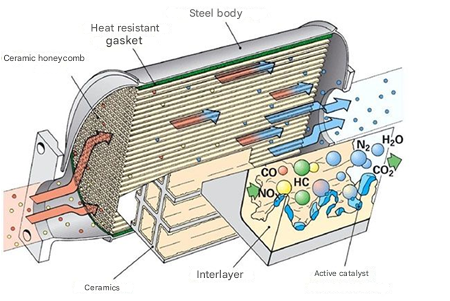
Principle of operation:
- Absorption of exhaust gases: When the engine is running, exhaust gases pass through the catalyst. It consists of a porous substrate, usually made of ceramics or metal, coated with a catalytic layer.
- Chemical reactions: Inside the catalyst, two main types of reactions occur:
- Oxidation reaction: Carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons are oxidized, converting into carbon dioxide and water.
- Reduction reaction: Nitrogen oxides are converted into nitrogen and oxygen.
- Efficiency: To achieve maximum efficiency, the catalyst must reach a certain operating temperature. Therefore, modern cars often use heaters to speed up this process.
- Durability: Over time, the catalyst can become contaminated and lose efficiency. That’s why it’s important to monitor the condition of the system and perform regular maintenance.
In conclusion, the catalyst plays a crucial role in ensuring the environmental friendliness of vehicles by helping to reduce the level of pollution in the environment.

